
A new study reveals an innovative approach to photon confinement in quantum nanophotonics, introducing nanocavities that extend photon lifetime while maintaining subwavelength volumes, promising new advancements in quantum applications. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
Dr. Hanan Herzig Sheinfux, from Bar-Ilan University: “What started as a chance discovery, may well open the way to new quantum applications, pushing the boundaries of what we thought was possible.”
In a significant leap forward for quantum nanophotonics, a team of European and Israeli physicists, introduces a new type of polaritonic cavities and redefines the limits of light confinement. This pioneering work, detailed in a study published today (February 6) in Nature Materials, demonstrates an unconventional method to confine photons, overcoming the traditional limitations in nanophotonics.
Physicists have long been seeking ways to force photons into increasingly small volumes. The natural length scale of the
This concentration enhances interactions with electrons, amplifying quantum processes within the cavity. However, despite significant success in confining light into deep subwavelength volumes, the effect of dissipation (optical absorption) remains a major obstacle.
Photons in nanocavities are absorbed very quickly, much faster than the wavelength, and this dissipation limits the applicability of nanocavities to some of the most exciting quantum applications.
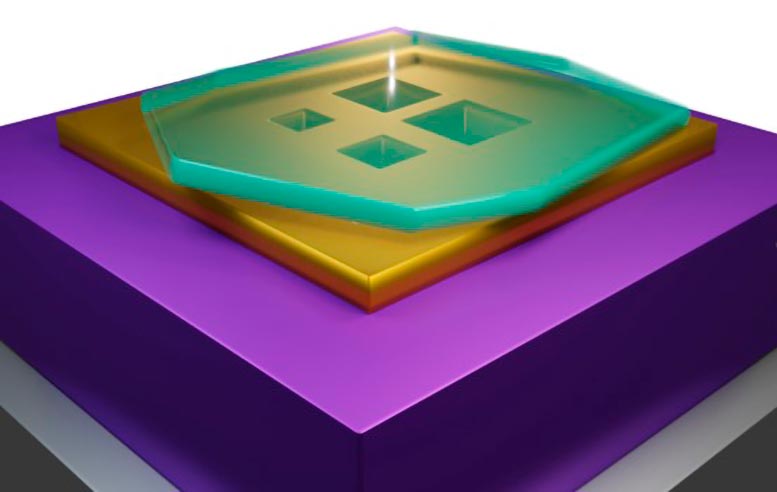
3D rendering of 4 polaritonic cavities of different sizes. Credit: Matteo Ceccanti
Innovative Nanocavity Design
The research group of Prof. Frank Koppens from ICFO in Barcelona, Spain, addressed this challenge by creating nanocavities with an unparalleled combination of subwavelength volume and extended lifetime.
These nanocavities, measuring smaller than 100x100nm² in area and only 3nm thin, confine light for significantly longer durations. The key lies in the use of hyperbolic-phonon-polaritons, unique electromagnetic excitations occurring in the 2D material forming the cavity.
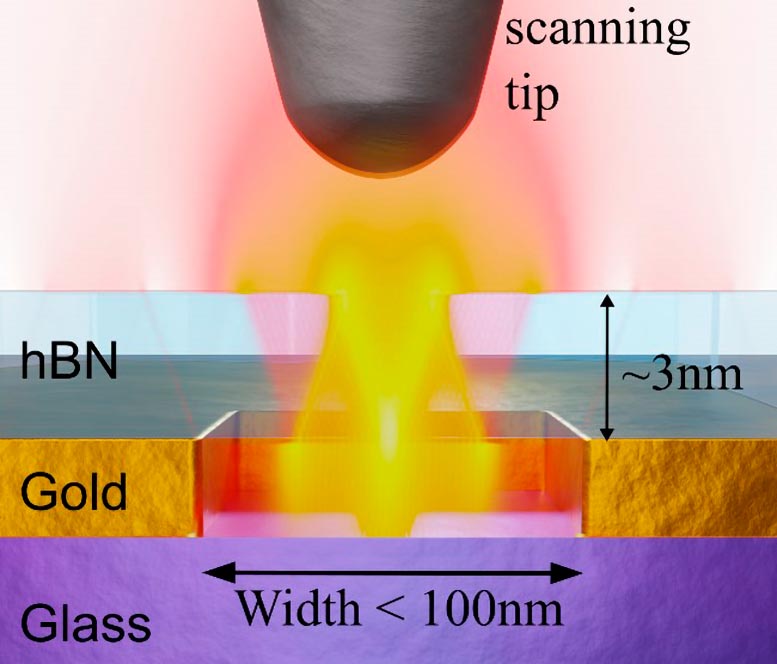
Sketch of a nanocavity (cross-section view) and the nearfield tip, superimposed with the simulated ray-like field distribution of the cavity modes. Credit: Matteo Ceccanti
Unlike previous studies on phonon polariton-based cavities, this work utilizes a new and indirect confinement mechanism. The nanocavities are crafted by drilling 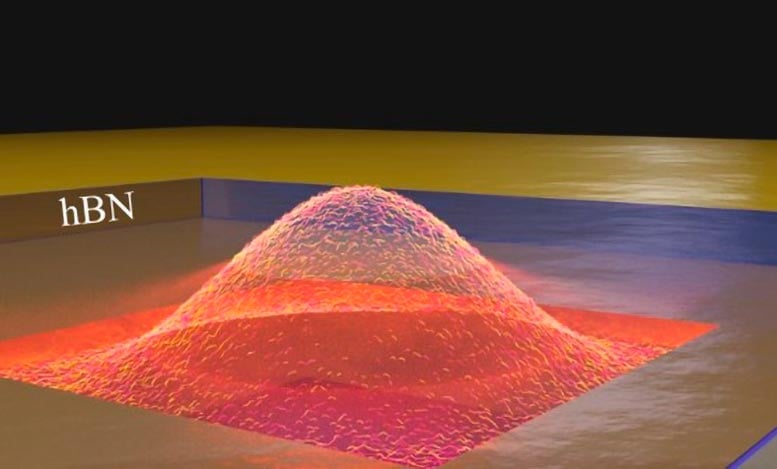
Artist’s impression of a nanocavity and the field inside it. Credit: Matteo Ceccanti