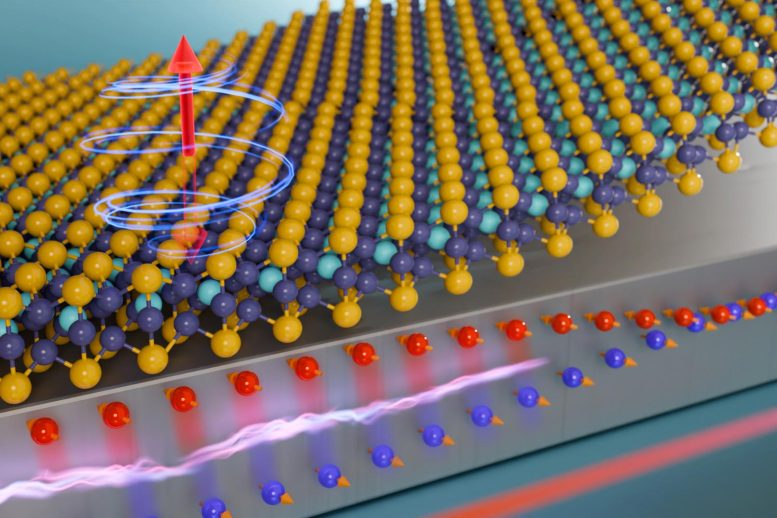
This illustration shows electric current being pumped into platinum (the bottom slab), which results in the creation of an electron spin current that switches the magnetic state of the 2D ferromagnet on top. The colored spheres represent the atoms in the 2D material. Credit: Courtesy of the researchers
An
This is key, since magnets composed of atomically thin van der Waals materials can typically only be controlled at extremely cold temperatures, making them difficult to deploy outside a laboratory.
The researchers used pulses of electrical current to switch the direction of the device’s magnetization at room temperature. Magnetic switching can be used in computation, the same way a transistor switches between open and closed to represent 0s and 1s in binary code, or in computer memory, where switching enables data storage.
The team fired bursts of electrons at a magnet made of a new material that can sustain its magnetism at higher temperatures. The experiment leveraged a fundamental property of electrons known as spin, which makes the electrons behave like tiny magnets. By manipulating the spin of electrons that strike the device, the researchers can switch its magnetization.
“The heterostructure device we have developed requires an order of magnitude lower electrical current to switch the van der Waals magnet, compared to that required for bulk magnetic devices,” says Deblina Sarkar, the AT&T Career Development Assistant Professor in the MIT Media Lab and Center for Neurobiological Engineering, head of the Nano-Cybernetic Biotrek Lab, and the senior author of a paper on this technique. “Our device is also more energy efficient than other van der Waals magnets that are unable to switch at room temperature.”
In the future, such a magnet could be used to build faster computers that consume less electricity. It could also enable magnetic computer memories that are nonvolatile, which means they don’t leak information when powered off, or processors that make complex AI algorithms more energy-efficient.
“There is a lot of inertia around trying to improve materials that worked well in the past. But we have shown that if you make radical changes, starting by rethinking the materials you are using, you can potentially get much better solutions,” says Shivam Kajale, a graduate student in Sarkar’s lab and co-lead author of the paper.
Kajale and Sarkar are joined on the paper by co-lead author Thanh Nguyen, a graduate student in the Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering (NSE); Corson Chao, a graduate student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering (DSME); David Bono, a DSME research scientist; Artittaya Boonkird, an NSE graduate student; and Mingda Li, associate professor of nuclear science and engineering. The research was published recently in SciTechDaily