Artificial intelligence, particularly through machine learning, is revolutionizing how we solve complex problems in various fields including science, medicine, and technology. Facilities like Argonne National Laboratory are leading these advancements, using AI to predict complex system behaviors, improve material selection, and assist in global challenges like disease and climate change.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the collective term for computer technologies and techniques that help solve complex problems by imitating the brain’s ability to learn.
AI helps computers recognize patterns hidden within a lot of information, solve problems, and adjust to changes in processes as they happen, much faster than humans can.
In this Science 101: What is Artificial Intelligence video, Argonne National Laboratory scientists Taylor Childers and Bethany Lusch discuss AI — the computer technologies and techniques that help solve complex problems by imitating the brain’s ability to learn. Researchers use AI to be better and faster at tackling the most difficult problems in science, medicine, and technology, and help drive discovery in those areas. This could range from helping us understand how
Researchers use AI to be better and faster at tackling the most difficult problems in science, medicine, and technology, and help drive discovery in those areas. This could range from helping us understand how COVID-19 attacks the human body to finding ways to manage traffic jams.
Many Department of Energy (DOE) facilities, like Argonne National Laboratory, assist in developing some the most advanced AI technologies available. Today, they are used in areas of study ranging from chemistry to environmental and manufacturing sciences to medicine and the universe.
AI is used to help make models of complex systems, like engines or weather, and predict what might happen if certain parts of those systems changed — for example, if a different fuel was used or temperatures increased steadily.
But there are many more uses for AI.
A key tool in Argonne’s AI toolbox is a type of technique called machine learning that gets smarter or more accurate as it gets more data to learn from. Machine learning is really helpful in identifying specific objects hidden within a bigger, more crowded picture.
In a popular example, a 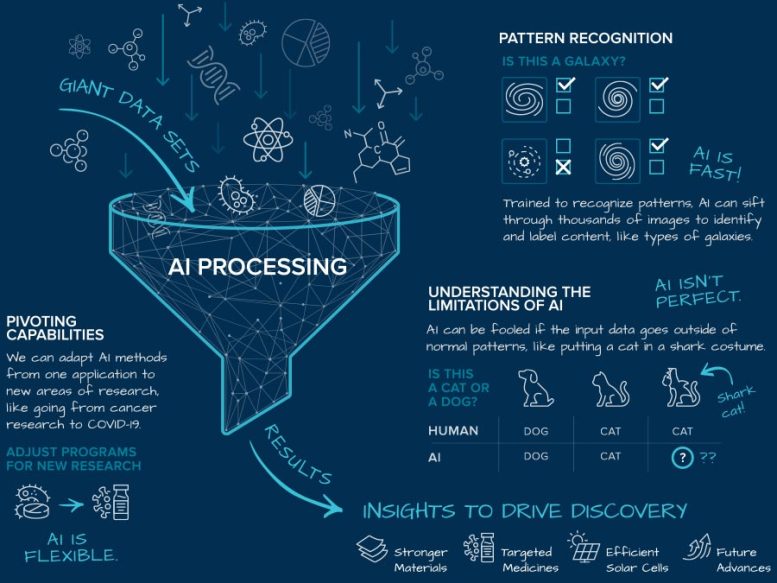
Credit: Argonne National Laboratory