
A method for stabilizing the interfaces in solid-state lithium-ion batteries opens new possibilities.
In the endless quest to pack more energy into batteries without increasing their weight or volume, one especially promising technology is the solid-state battery. In these batteries, the usual liquid electrolyte that carries charges back and forth between the electrodes is replaced with a solid electrolyte layer. Such batteries could potentially not only deliver twice as much energy for their size, they also could virtually eliminate the fire hazard associated with today’s lithium-ion batteries.
But one thing has held back solid-state batteries: Instabilities at the boundary between the solid electrolyte layer and the two electrodes on either side can dramatically shorten the lifetime of such batteries. Some studies have used special coatings to improve the bonding between the layers, but this adds the expense of extra coating steps in the fabrication process. Now, a team of researchers at 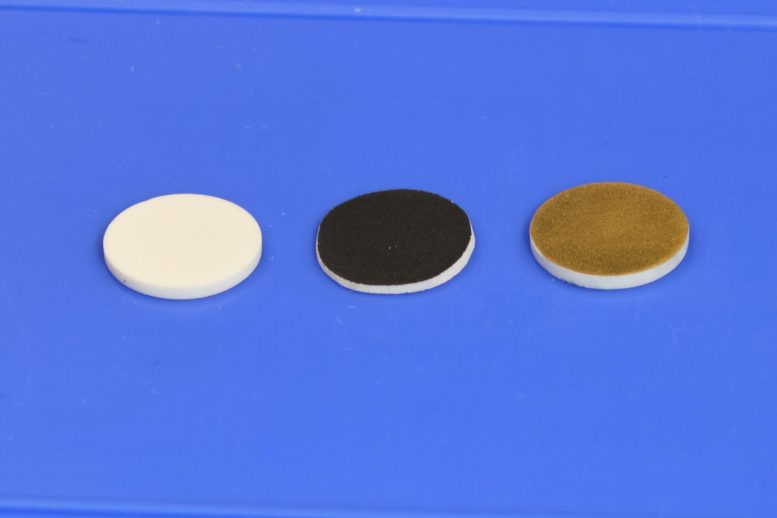
These discs were used for testing the researchers’ processing method for solid-electrolyte batteries. On the left, a sample of the solid electrolyte itself, a material known as LLPO. At center, the same material coated with the cathode material used in their tests. At right, the LLPO material with a coating of gold, used to facilitate measuring its electrical properties. Credit: Pjotrs Žguns
The new method simply requires eliminating any carbon dioxide present during a critical manufacturing step, called sintering, where the battery materials are heated to create bonding between the cathode and electrolyte layers, which are made of ceramic compounds. Even though the amount of carbon dioxide present is vanishingly small in air, measured in parts per million, its effects turn out to be dramatic and detrimental. Carrying out the sintering step in pure oxygen creates bonds that match the performance of the best coated surfaces, without that extra cost of the coating, the researchers say.
The findings are reported in the journal Advanced Energy Materials, in a paper by MIT doctoral student Younggyu Kim, professor of nuclear science and engineering and of materials science and engineering Bilge Yildiz, and Iradikanari Waluyo and Adrian Hunt at Brookhaven National Laboratory.
“Solid-state batteries have been desirable for different reasons for a long time,” Yildiz says. “The key motivating points for solid batteries are they are safer and have higher energy density,” but they have been held back from large scale commercialization by two factors, she says: the lower conductivity of the solid electrolyte, and the interface instability issues.
The conductivity issue has been effectively tackled, and reasonably high-conductivity materials have already been demonstrated, according to Yildiz. But overcoming the instabilities that arise at the interface has been far more challenging. These instabilities can occur during both the manufacturing and the electrochemical operation of such batteries, but for now the researchers have focused on the manufacturing, and specifically the sintering process.
Sintering is needed because if the ceramic layers are simply pressed onto each other, the contact between them is far from ideal, there are far too many gaps, and the electrical resistance across the interface is high. Sintering, which is usually done at temperatures of 1,000 degrees