
Researchers at POSTECH, led by Professor Kyu-Young Park, have developed a new single-crystal synthesis technology for nickel-based cathode materials in electric vehicle batteries, demonstrating significantly enhanced lifespan and durability. Their work, published in ACS Materials & Interfaces, highlights the critical temperature needed for synthesizing robust single crystals, contributing to more durable and efficient batteries.
POSTECH researchers have advanced electric vehicle battery technology by developing a method to synthesize durable single-crystal cathode materials, extending battery life and efficiency.
Could high-temperature single crystals enable electric vehicles capable of traveling up to one million kilometers?
A team from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), under the leadership of Professor Kyu-Young Park of the Graduate Institute of Ferrous & Eco Materials Technology and the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, together with PhD candidate Kyoung Eun Lee and alumna Yura Kim, has made a significant advancement. Collaborating with POSCO Holdings N.EX.T Hub, they have successfully developed a single-crystal synthesis technology that greatly enhances the longevity of cathode materials used in electric vehicles.
This research was published in the online edition of ACS Materials & Interfaces, an international journal in the materials science field.
Lithium (Li) secondary batteries, commonly used in electric vehicles, store energy by converting electrical energy to chemical energy and generating electricity to release chemical energy to electrical energy through the movement of Li- ions between a cathode and an anode. These secondary batteries mainly use nickel (Ni) cathode materials due to their high lithium-ion storage capacity. Traditional nickel-based materials have a polycrystalline morphology composed of many tiny crystals that can undergo structural degradation during charging and discharging, significantly reducing their lifespan.
The Benefits of Single-Crystal Cathode Materials
One approach to addressing this issue is to produce the cathode material in a “single-crystal” form. Creating nickel-based cathode materials as single large particles, or “single crystals,” can enhance their structural and chemical stability and durability. It is known that single-crystal materials are synthesized at high temperatures and become rigid. However, the exact process of hardening during synthesis and the specific conditions under which this occurs remains unclear.
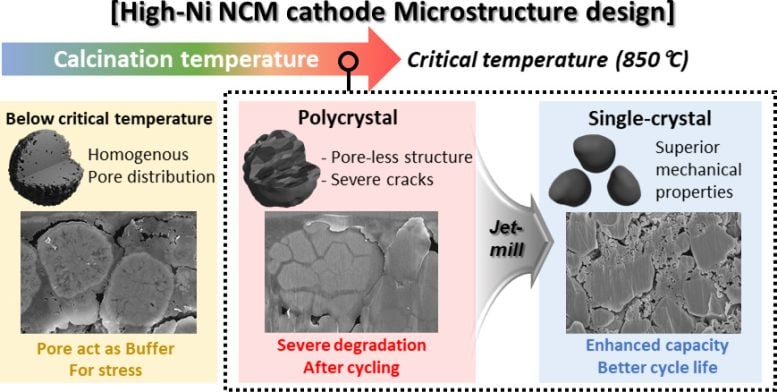
Schematic of the microstructure evolution of high-nickel cathode materials with synthesis temperature and a strategy for synthesizing single crystals at a critical temperature. Credit: POSTECH
To improve the durability of nickel cathode materials for electric vehicles, the researchers focused on identifying a specific temperature, referred to as the “critical temperature,” at which high-quality single-crystal materials are synthesized. They investigated various synthesis temperatures to determine the optimal conditions for forming single crystals in the synthesis of a nickel-based cathode material (N884). The team systematically observed the impact of temperature on the material’s capacity and long-term performance.
The researchers discovered that conventional polycrystalline materials synthesized below a certain critical temperature are prone to degradation with prolonged use in secondary batteries. However, when synthesized above this critical temperature, high-quality single crystals can be easily produced, leading to materials with superior longevity.
This is due to a process called “densification“ which occurs above a certain critical temperature. During this process, the internal grain size of the material increases and the empty spaces within the material are densely filled. Densified single crystals are extremely hard and resistant to degradation over extended periods, significantly enhancing their durability. Based on these findings, the team confirmed that synthesizing single crystals above the critical temperature is a more advantageous material design strategy. They also proposed an effective method for synthesizing high-quality single crystal materials.
Professor Kyu-Young Park of POSTECH stated, “We have introduced a new synthesis strategy to enhance the durability of nickel-based cathode materials.” He added, “We will continue our research to make secondary batteries for electric vehicles cheaper, faster, and longer-lasting.”
Reference: “Comparison Study of a Thermal-Driven Microstructure in a High-Ni Cathode for Lithium-Ion Batteries: Critical Calcination Temperature for Polycrystalline and Single-Crystalline Design” by Kyoung Eun Lee, Yura Kim, Ju Seong Kim, Kyoung Sun Kim, Ki Joo Hong, Sang-Cheol Nam, Hyungsub Kim, Dongwook Lee and Kyu-Young Park, 29 April 2024, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.DOI: 10.1021/acsami.4c00514
The research was conducted with support from the POSCO Holdings and the Basic Research Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Source: SciTechDaily