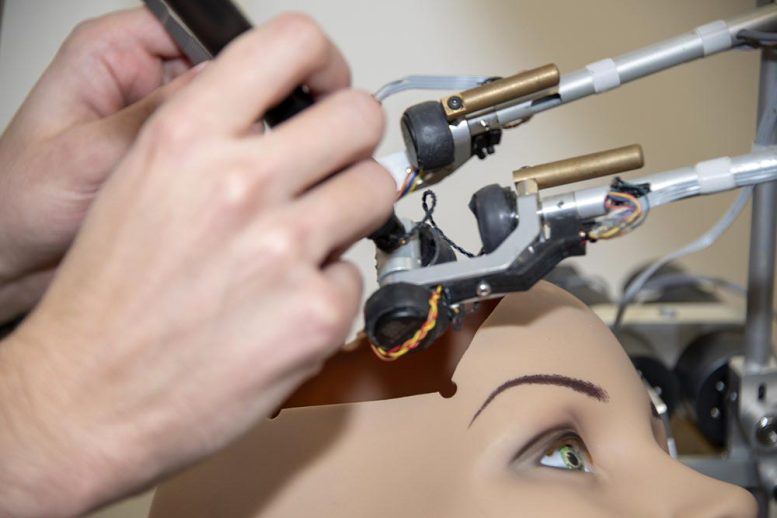
A student training on a neurosurgical simulator. Credit: The Neuro
Machine learning algorithms enhanced technical performance and learning outcomes during simulated brain tumor removal.
The
An AI-powered tutor called the Virtual Operative Assistant (VOA) used a machine learning algorithm to teach safe and efficient surgical technique and provided personalized feedback, while a deep learning Intelligent Continuous Expertise Monitoring System (ICEMS) and a panel of experts assessed student performance.
In the other group, remote instructors watched a live feed of the surgical simulations and provided feedback based on the student’s performance.
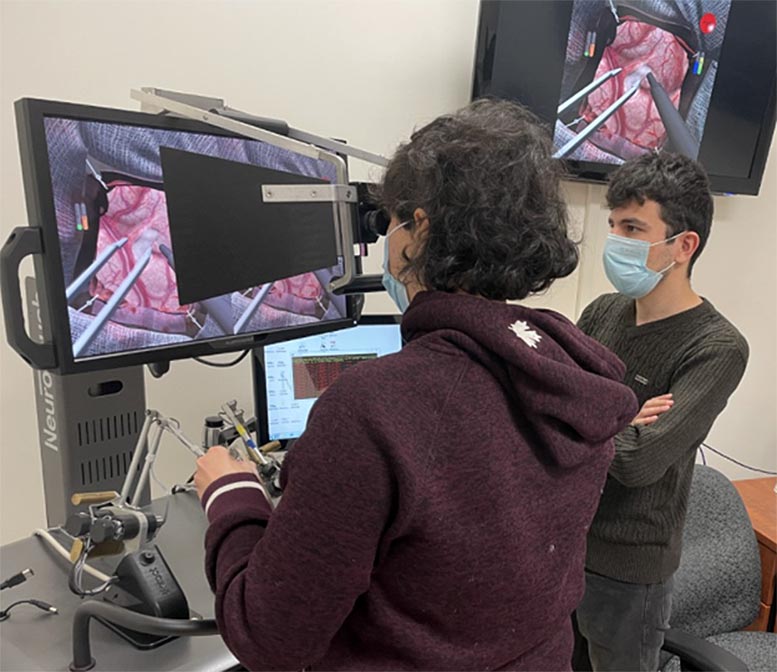
A student training on a neurosurgical simulator. Credit: The Neuro
The researchers found that students who received VOA instruction and feedback learned surgical skills 2.6 times faster and achieved 36 percent better performance compared to those who received instruction and feedback from remote instructors. And while researchers expected students instructed by VOA to experience greater stress and negative emotion, they found no significant difference between the two groups.
Surgical skill plays an important role in patient outcomes both during and after brain surgery. VOA may be an effective way to increase neurosurgeon performance, improving patient safety while reducing the burden on human instructors.
“Artificially intelligent tutors like the VOA may become a valuable tool in the training of the next generation of neurosurgeons,” says Dr. Rolando Del Maestro, the study’s senior author. “The VOA significantly improved expertise while fostering an excellent learning environment. Ongoing studies are assessing how in-person instructors and AI-powered intelligent tutors can most effectively be used together to improve the mastery of neurosurgical skills.”
“Intelligent tutoring systems can use a variety of simulation platforms to provide almost unlimited chances for repetitive practice without the constraints imposed by the availability of supervision,” says Ali Fazlollahi, the study’s first author. “With continued research, increased development, and dissemination of intelligent tutoring systems, we can be better prepared for ever-evolving future challenges.”
Reference: “Effect of Artificial Intelligence Tutoring versus Expert Instruction on Learning Simulated Surgical Skills Among Medical Students: A Randomized Clinical Trial” 22 February 2022, JAMA Network Open.DOI: 10.1017/cjn.2020.202
This study, published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA Network Open) on February 22, 2022, was funded by the Franco Di Giovanni Foundation, the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada, and the Brain Tumour Foundation of Canada Tumour Research Grant along with The Neuro. Cognitive assessment was led by Dr. Jason Harley at McGill University’s Department of Surgery.
The Neuro
The Neuro – The Montreal Neurological Institute-Hospital – is a bilingual, world-leading destination for brain research and advanced patient care. Since its founding in 1934 by renowned neurosurgeon Dr. Wilder Penfield, The Neuro has grown to be the largest specialized neuroscience research and clinical center in Canada, and one of the largest in the world. The seamless integration of research, patient care, and training of the world’s top minds make The Neuro uniquely positioned to have a significant impact on the understanding and treatment of nervous system disorders. In 2016, The Neuro became the first institute in the world to fully embrace the Open Science philosophy, creating the Tanenbaum Open Science Institute. The Montreal Neurological Institute is a McGill University research and teaching institute. The Montreal Neurological Hospital is part of the Neuroscience Mission of the McGill University Health Centre.